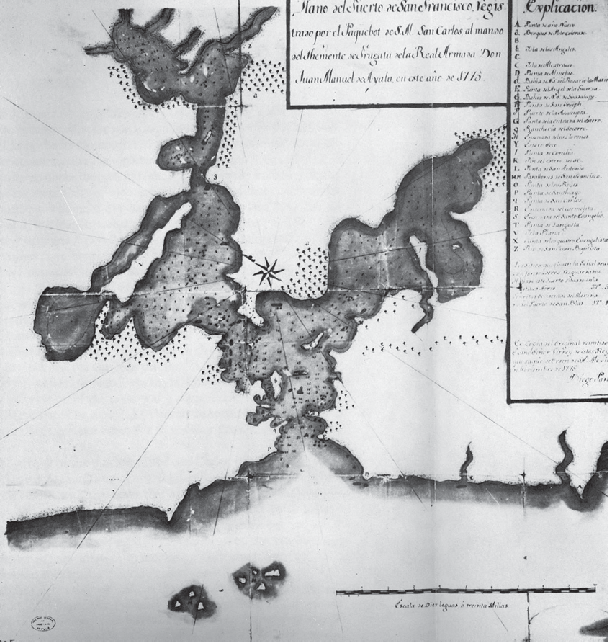
n 1775, Spanish explorer Juan Manuel de Ayala (1745-97) mapped and named rugged Alcatraz Island, christening it La Isla de los Alcatraces, or Island of the Pelicans, due to its large population of sea birds. It is rumored, though, that the name was intended for the nearby Yuba island. Alcatraz actually had very few pelicans on it. I guess maps were not very accurate in 1775.
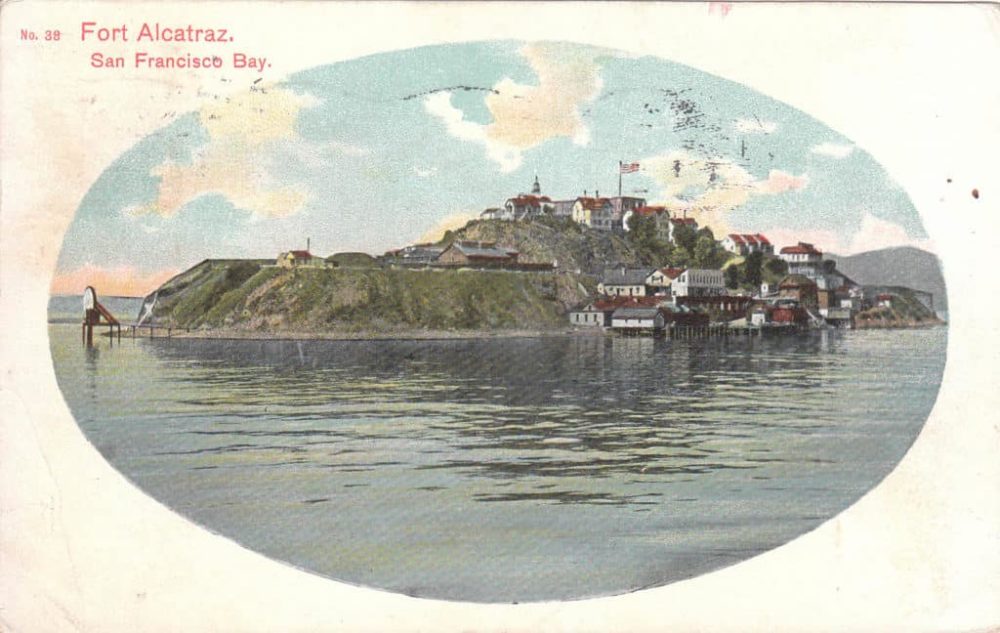
Seventy-five years later, in 1850, an order was signed reserving the island for military use. During the 1850s, a fortress was constructed on Alcatraz and some 100 cannons were installed around the island to protect San Francisco Bay. Also during this time, Alcatraz became home to the West Coast’s first operational lighthouse.
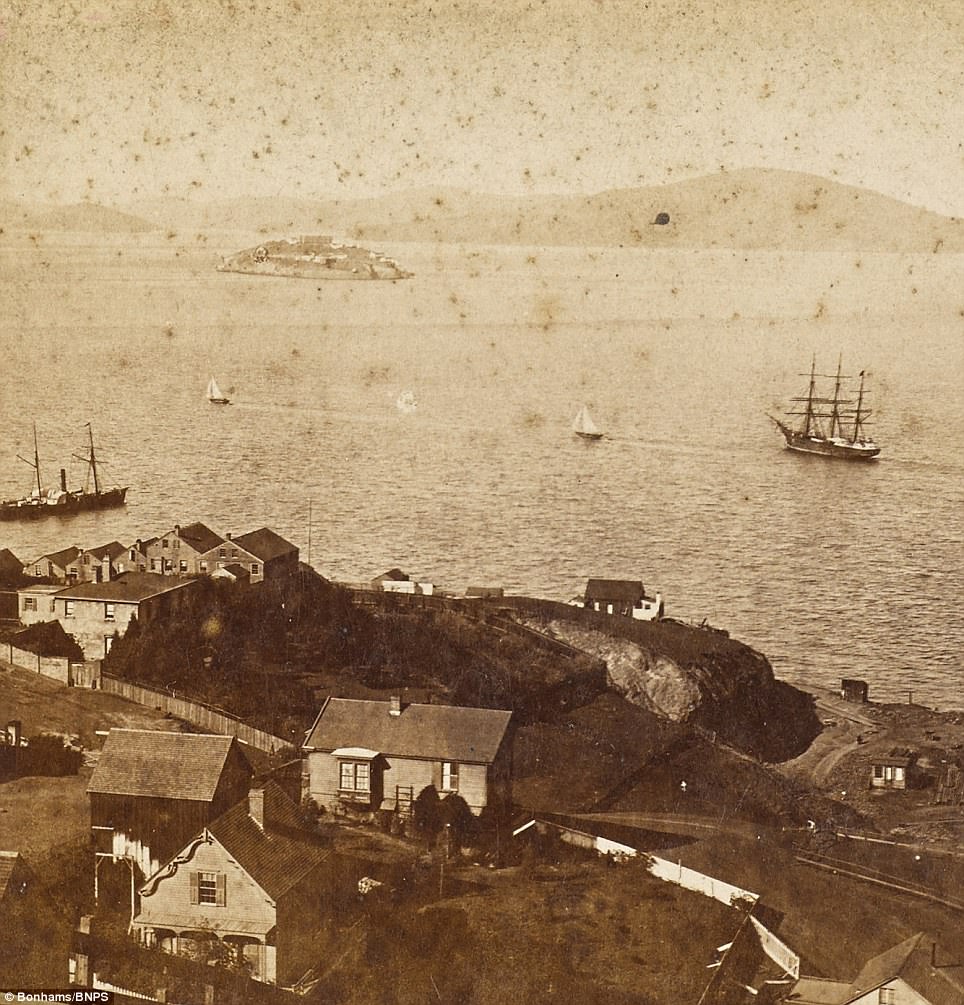
By the late 1850s, the U.S. Army had begun holding military prisoners at Alcatraz. Isolated from the mainland by the cold, strong waters of San Francisco Bay, the island was deemed an ideal location for a prison. It was assumed no Alcatraz inmate could attempt to escape by swimming and survive.
During its years as a military prison, the inmates at Alcatraz included Confederate sympathizers and citizens accused of treason during the Civil War.

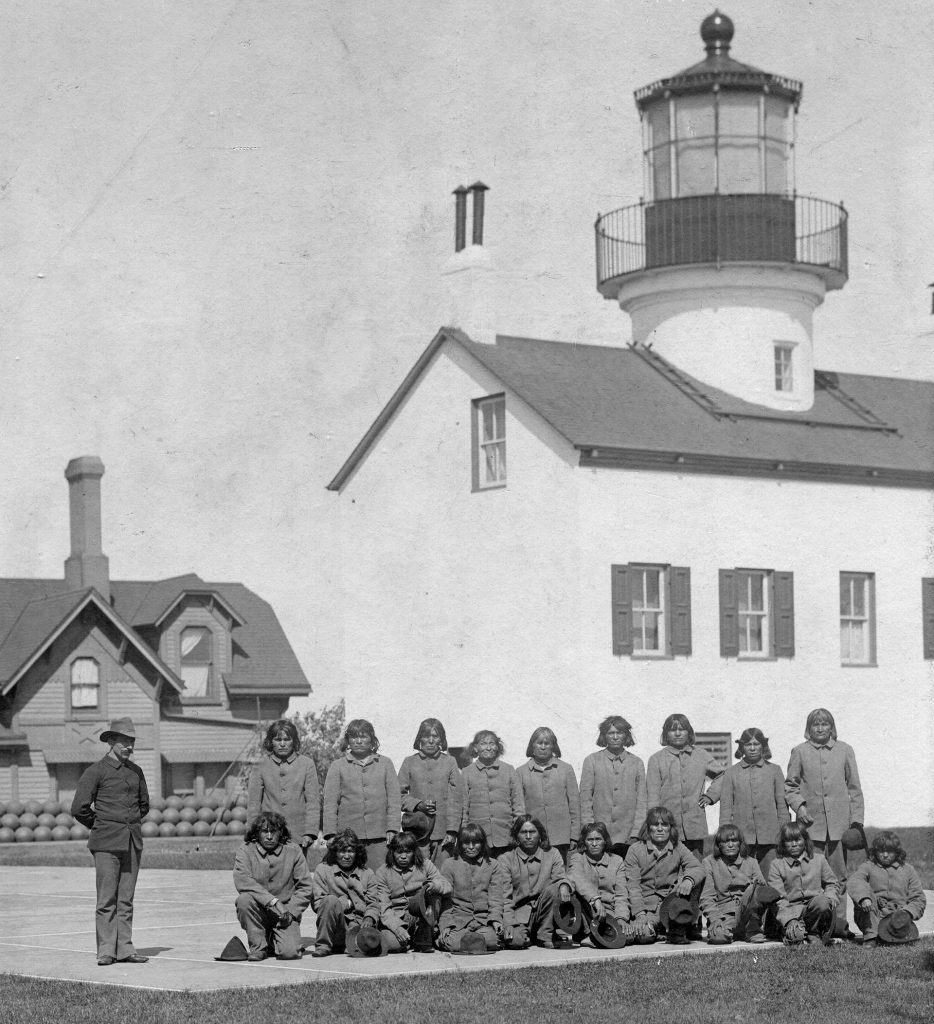
Alcatraz also housed a number of “rebellious” American Indians, including 19 Hopis from the Arizona Territory who were sent to the prison in 1895 following land disagreements with the federal government. The inmate population at Alcatraz continued to rise during the Spanish-American War.

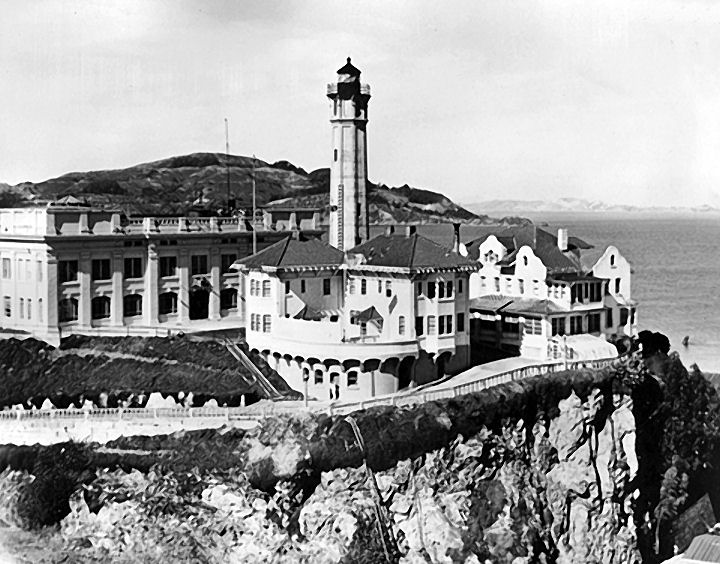
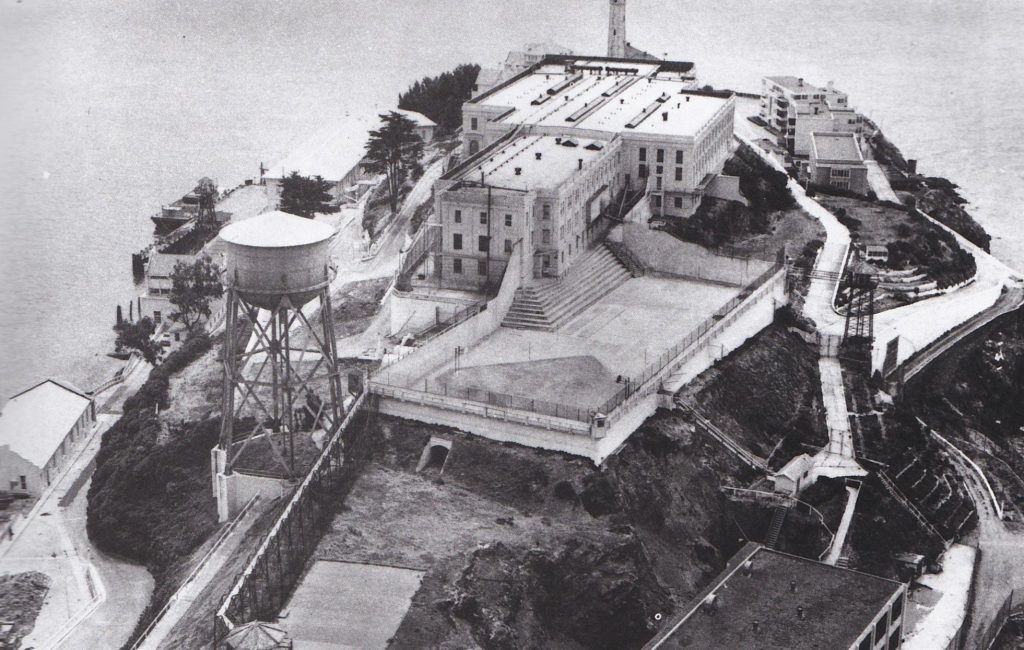
During the early 20th century, inmate labor fueled the construction of a new cellhouse (the 600-cell structure still stands today) on Alcatraz, along with a hospital, mess hall and other prison buildings. According to the National Park Service, when this new complex was finished in 1912 it was the world’s largest reinforced concrete building.

In 1933, the Army relinquished Alcatraz to the U.S. Justice Department, which wanted a federal prison that could house a criminal population too difficult or dangerous to be handled by other U.S. penitentiaries. Following construction to make the existing complex at Alcatraz more secure, the maximum-security facility officially opened on July 1, 1934. The first warden, James A. Johnston (1874-1954), hired approximately one guard for every three prisoners. Each prisoner had his own cell.

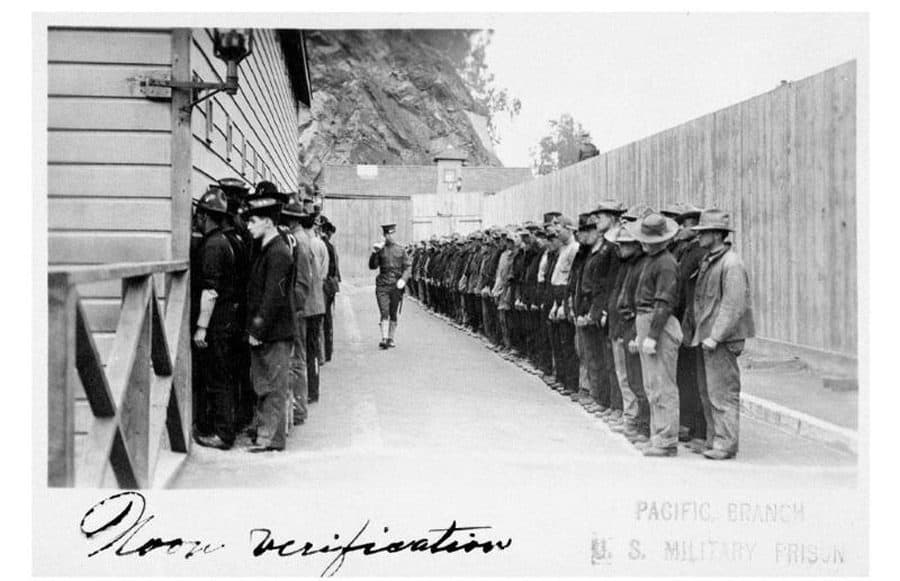
The Federal Bureau of Prisons viewed Alcatraz as “the prison system’s prison,” a place where the most disruptive inmates could be sent to live under sparse conditions with few privileges in order to learn how to follow rules (at which point, they could be transferred to other federal prisons to complete their sentences). According to the Bureau of Prisons, Alcatraz typically held some 260 to 275 prisoners, which represented less than 1 percent of the entire federal inmate population.
The federal penitentiary at Alcatraz was shut down in 1963 because its operating expenses were much higher than those of other federal facilities at the time. (The prison’s island location meant all food and supplies had to be shipped in, at great expense.) Furthermore, the isolated island buildings were beginning to crumble due to exposure to the salty sea air. During nearly three decades of operation, Alcatraz housed a total of 1,576 men.
In March 1964 a group of Native Americans claimed the island, citing an 1868 treaty with the Sioux allowing Indians from the reservation to claim any “unoccupied government land”; however, they occupied Alcatraz for only several hours. In 1969, a group of Native Americans led by Mohawk activist Richard Oakes arrived on Alcatraz Island and claimed the land on behalf of “Indians of All Tribes.” The activists hoped to establish a university and a museum on the island. Oakes left Alcatraz following the death there of his stepdaughter in 1970 and the remaining occupiers, whose ranks had become increasingly contentious and divided, were removed by order of President Nixon 1971. The island became part of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area in 1972 and was opened to the public a year later.